Engineering Context
Medical ventilators are life-critical devices that must operate continuously, accurately, and safely under strict regulatory and environmental constraints. At the core of these systems lies the medical ventilator PCB assembly, which integrates power management, sensor interfaces, control processors, communication modules, and alarm systems into a compact and highly reliable electronic platform.
Unlike consumer electronics, medical PCB assemblies are required to maintain long-term stability, electrical accuracy, and mechanical integrity over extended operating cycles, frequent sterilization procedures, and demanding hospital environments. This article analyzes medical ventilator PCB assembly from an engineering perspective, focusing on material science, stackup architecture, signal and power integrity, and reliability validation aligned with medical device requirements.
Core Engineering Challenges
Medical ventilator PCB assemblies face a unique set of engineering challenges that distinguish them from industrial or consumer electronics.
Continuous operation and reliability are the primary concerns. Ventilators often operate 24/7, with minimal tolerance for electrical drift, thermal degradation, or intermittent failures. PCB materials, solder joints, and vias must support long duty cycles without performance degradation.
Signal integrity and sensor accuracy are equally critical. Ventilators rely on precise pressure, flow, oxygen concentration, and temperature sensing. Any noise, impedance discontinuity, or EMI coupling within the PCB assembly can directly impact patient safety.
Power integrity and redundancy present another challenge. Medical ventilator PCBs integrate multiple voltage domains powering microcontrollers, motor drivers, displays, and communication interfaces. Stable power delivery with minimal ripple is essential for system reliability.
Additionally, EMI control and regulatory compliance are mandatory. Medical devices must meet stringent EMC standards to prevent interference with other hospital equipment while remaining immune to external noise sources.
Material Science & Dielectric Performance
Material selection plays a decisive role in medical ventilator PCB assembly, particularly in achieving long-term electrical stability and manufacturability.
High-reliability FR-4 variants with controlled glass weave, low ionic contamination, and stable dielectric properties are commonly used for medical PCB designs. For sections involving high-speed communication or RF modules, low-loss RF PCB materials may be selectively applied.
Typical Material Parameters
| Parameter | Medical-Grade PCB Material | Engineering Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Constant (Dk) | 3.6 – 4.2 | Stable signal timing |
| Dissipation Factor (Df) | ≤0.012 | Reduced signal loss |
| Tg | ≥170 °C | Thermal endurance |
| CTI | ≥600 V | Electrical safety |
| Z-axis CTE | ≤70 ppm/°C | Via reliability |
Material consistency is essential to avoid drift in impedance-controlled traces and sensor interfaces. Low-loss and stable dielectric behavior also helps maintain predictable signal integrity across temperature variations commonly encountered during long-term operation.
GOPCBA Case Study — Medical Ventilator PCB
Customer Background
A medical equipment manufacturer developing a new generation ICU ventilator required a high-reliability PCB assembly solution. The ventilator PCB integrated control logic, motor drive circuits, multiple sensor inputs, and communication interfaces within a compact enclosure designed for continuous hospital use.
Engineering Problems
-
Signal noise affecting pressure and flow sensor accuracy
-
Power rail instability during motor load transients
-
EMI emissions exceeding medical EMC limits
-
Reliability concerns under long-term thermal stress
GOPCBA Solution
GOPCBA delivered a medical ventilator PCB assembly solution emphasizing material control, optimized stackup, and assembly process validation. Special attention was given to power integrity, analog-digital isolation, and EMI suppression.
Measured Performance Results
| Test Item | Requirement | Measured Result |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor Signal Noise | ≤1% FS | 0.4% FS |
| Power Ripple | ≤50 mV | 18 mV |
| EMI Emission Margin | ≥6 dB | 11 dB |
| Assembly Yield | ≥99% | 99.6% |
The validated medical PCB assembly met functional, electrical, and regulatory requirements for ventilator applications.
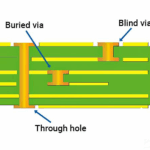
Stackup Design & RF Implementation
Stackup design is a fundamental aspect of medical ventilator PCB assembly, directly influencing signal integrity, power stability, and EMI control.
Example Medical Ventilator PCB Stackup
| Layer | Function | Material |
|---|---|---|
| L1 | Signal / Components | Medical-Grade FR-4 |
| L2 | Solid Ground Plane | Copper |
| L3 | Power Plane | Copper |
| L4 | Control & Sensor Signals | Medical-Grade FR-4 |
| L5 | Ground Plane | Copper |
| L6 | Low-Speed Signals | Medical-Grade FR-4 |
This stackup ensures short return paths, controlled impedance, and effective isolation between analog sensor signals and digital control circuitry. Where wireless connectivity is required, localized RF PCB materials are integrated with impedance-controlled traces.
Simulation using ADS and TDR analysis verified impedance control, while power integrity simulations confirmed stable voltage delivery under dynamic motor loads.

Environmental & Reliability Validation
Medical ventilator PCB assemblies must pass rigorous environmental and reliability validation to ensure safe long-term use.
Reliability Test Summary
| Test Type | Condition | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Cycling | −20 °C ↔ 70 °C, 500 cycles | Pass |
| High-Temp Operating Life | 85 °C, 1000 hrs | Pass |
| Humidity Exposure | 85 °C / 85% RH | Pass |
| Vibration | Medical transport profile | Pass |
| Solder Reflow | 3× @ 260 °C | No defects |
Thermal FEM analysis confirmed uniform heat distribution across power components, reducing localized stress and improving solder joint longevity.
These validation results demonstrate that the medical ventilator PCB assembly meets both functional and regulatory expectations for life-support equipment.
Engineering Summary & Contact
Medical ventilator PCB assembly demands a reliability-first engineering approach, combining stable materials, optimized stackup design, precise assembly processes, and comprehensive validation. By addressing signal integrity, power stability, EMI control, and environmental robustness, high-quality medical PCB assemblies can support safe and continuous ventilator operation in critical care environments.
GOPCBA provides engineering-driven medical PCB assembly services, including material selection support, stackup optimization, simulation, and reliability validation for medical ventilators and other life-critical medical electronics.