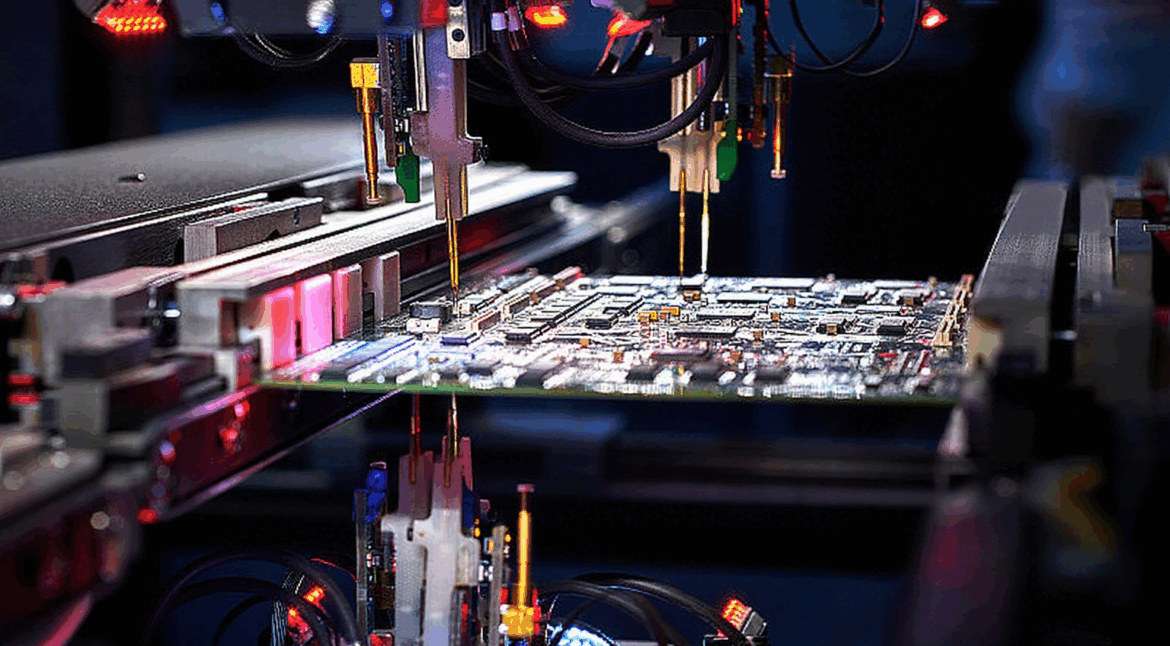
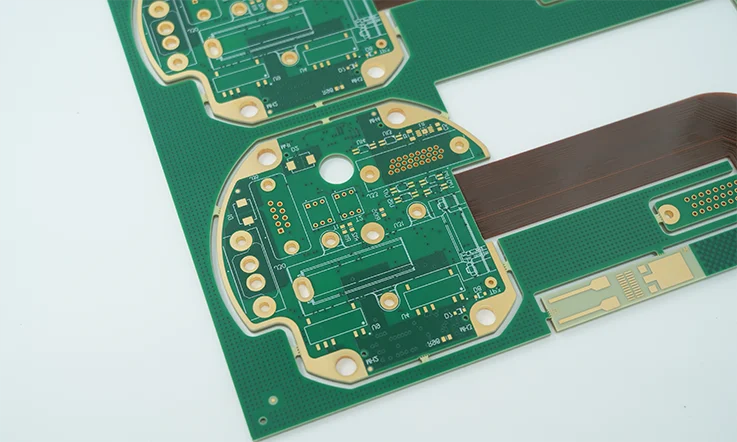
Engineering Context Thermal Management and CTE Control of Medical Ventilator PCB Assemblies for Long-Term Continuous Operation in ICU Devices defines the engineering baseline for ensuring stable respiratory control, signal integrity, and mechanical reliability in intensive care environments. ICU ventilators operate continuously for extended periods, where Medical Ventilator PCB Assemblies are…
Engineering Context Modern healthcare IoT systems integrate medical ventilators with smart gateways and wireless routers to enable real-time monitoring, telemedicine, and hospital-wide device coordination. PCB assemblies in these systems must support low-latency digital and RF communication, robust EMI suppression, and precise phase stability to maintain patient safety and operational reliability.…
Engineering Context Medical ventilators and hospital respiratory monitoring platforms operate in mission-critical environments where PCB assemblies must maintain signal integrity, precise control, and robust EMI suppression under continuous operation. High-density sensor interfaces, motor control circuits, and RF telemetry modules are sensitive to electromagnetic interference, thermal stress, and mechanical vibration. Kingda…
Medical ventilators are mission-critical life support systems that demand high-reliability PCB assemblies with precise signal integrity and power integrity control. These systems integrate sensors, microcontrollers, motor drivers, high-speed communication interfaces, and safety-critical monitoring circuits that must operate with deterministic latency and minimal noise. Any degradation in insertion loss, impedance control,…
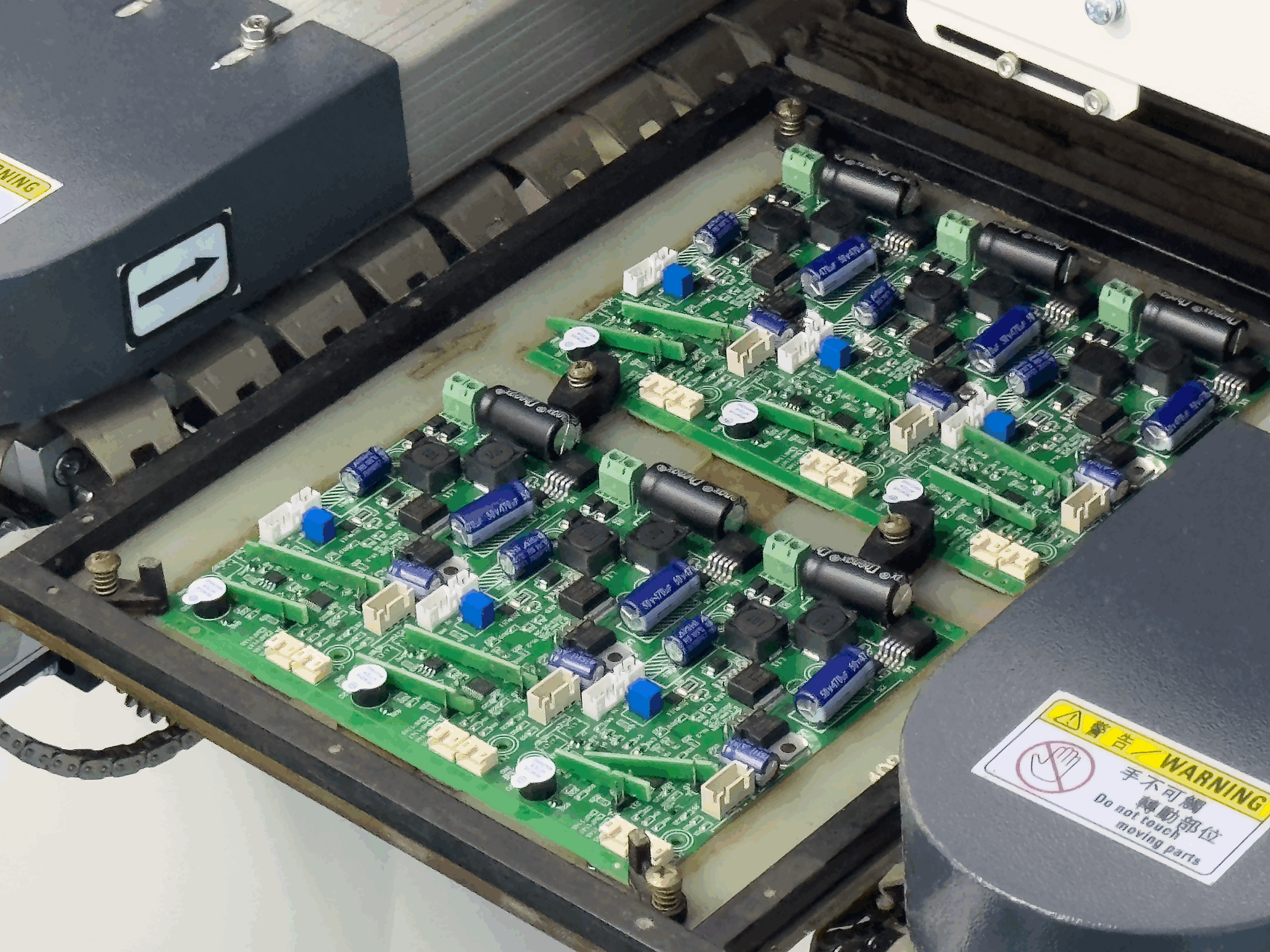
Medical Ventilator PCB Assembly is a mission-critical component in modern respiratory support systems. The performance, safety, and reliability of a ventilator directly depend on the quality of its PCB assembly. As an ISO 13485 certified manufacturer, Kingda delivers high-precision Medical Ventilator PCB Assembly solutions designed to meet strict medical safety…
Graphics Card BGA Assembly is a crucial step in the production of high-performance graphics cards. Industrial-grade PCBs made from CEM-4 material with a hybrid fiberglass-epoxy and polyimide resin structure ensure reliability, durability, and superior performance in demanding environments. This advanced PCB design guarantees: Excellent thermal stability for BGA soldering Mechanical…
Medical Device PCB Assembly demands exceptional precision and uncompromising reliability. In medical electronics, even minor defects in PCBs or PCBAs can cause device malfunction and pose serious risks to patient safety. As a result, engineers in the medical device industry place strong emphasis on rigorous process control, careful material selection,…
Engineering Context Power control electronics are core subsystems in industrial automation, motor drives, power supplies, energy conversion systems, and intelligent control platforms. These products integrate high-current switching devices, power management ICs, control processors, and communication interfaces on compact printed circuit boards. As power density increases, thermal stress and solder joint…
Engineering Context High-speed communication modules are fundamental components in modern networking equipment, data transmission systems, and industrial communication platforms. These modules integrate high-speed processors, RF interfaces, power management circuits, and dense interconnect structures within compact form factors. In such architectures, SMT PCB assembly is no longer a purely mechanical manufacturing…
Engineering Context Industrial communication equipment forms the backbone of modern factory automation, distributed control systems, and industrial IoT networks. From Ethernet-based fieldbus modules and industrial gateways to PLC communication cards and edge controllers, these systems rely on stable signal transmission and consistent manufacturing quality to ensure uninterrupted operation in electrically…