Engineering Context
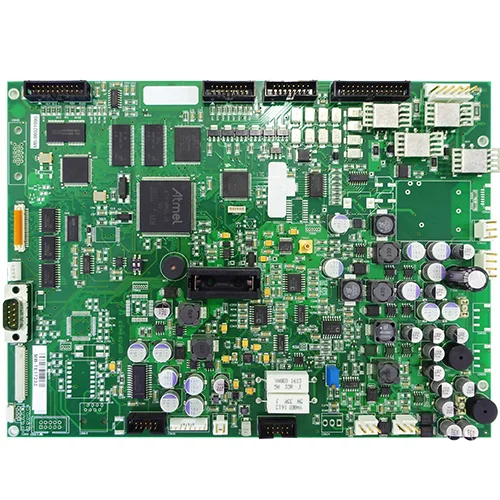
Motor drive systems and programmable logic controller (PLC) platforms are core elements of modern industrial automation, responsible for precise motion control, deterministic logic execution, and continuous system operation. The industrial PCB assembly used in these platforms must withstand high current transients, electrical noise, vibration, and long-term thermal stress while maintaining stable electrical performance and mechanical integrity.
Unlike consumer or light industrial electronics, motor drive and PLC PCB assemblies operate in electrically and mechanically aggressive environments. Switching power devices, inductive loads, and high-frequency control signals coexist on the same board, creating complex interactions between power integrity, signal integrity, and mechanical stress. This article analyzes how an engineering-driven industrial PCB assembly approach optimizes power integrity and mechanical robustness for motor drive and PLC platforms, integrating material science, stackup design, simulation, and comprehensive reliability validation.

Core Engineering Challenges
Industrial motor drive and PLC platforms introduce a unique combination of electrical and mechanical challenges that directly influence PCB assembly quality.
Power integrity under dynamic load conditions is a primary concern. Motor drives generate high di/dt and dv/dt switching events that can induce voltage ripple, ground bounce, and transient noise across the PCB. Poor assembly execution can exacerbate these effects through increased parasitic inductance or inconsistent solder joints.
Mechanical stress and vibration are unavoidable in industrial environments. Motors, gearboxes, and actuators transmit continuous vibration to control electronics. PCB assemblies must resist solder joint fatigue, via cracking, and connector loosening over extended operating lifetimes.
Thermal stress concentration presents another challenge. Power MOSFETs, IGBTs, gate drivers, and current sense components generate localized heat. Without mechanically robust assembly and effective thermal paths, repeated thermal cycling can degrade solder joints and laminate interfaces.
Finally, process consistency and manufacturability are critical for PLC platforms produced in volume. Variability in soldering quality, component placement, or via integrity can lead to inconsistent field behavior and increased maintenance costs.
Material Science & Dielectric Performance
Material selection establishes the mechanical and electrical foundation for industrial PCB assembly in motor drive and PLC applications.
High-Tg FR-4 materials are widely used due to their balanced performance, cost efficiency, and compatibility with mixed. For power-intensive designs, thicker cores and heavier copper weights are selected to improve current handling and thermal distribu SMT and through-hole assemblytion.
Typical Material Parameters for Motor Drive and PLC PCB Assembly
| Parameter | Typical Value | Engineering Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Constant (Dk) | 3.8 – 4.4 | Predictable control signal timing |
| Dissipation Factor (Df) | ≤0.015 | Reduced switching loss impact |
| Glass Transition (Tg) | ≥170 °C | Thermal endurance |
| Copper Thickness | 1–3 oz | Current capacity |
| Z-axis CTE | ≤70 ppm/°C | Via and solder joint reliability |
Stable dielectric behavior supports consistent impedance for control and communication signals, while low Z-axis CTE minimizes stress accumulation in plated through-holes during thermal cycling. Surface finishes such as ENIG or ENEPIG are commonly used to ensure uniform solderability and durable connector interfaces.
GOPCBA Case Study — Motor Drive and PLC Control PCB
Customer Background
A manufacturer of industrial motor drives and PLC systems required an industrial PCB assembly solution for a compact control module integrating power conversion, motor control logic, and industrial communication interfaces. The PCB was designed for continuous operation in factory environments with high vibration and temperature variation.
Engineering Problems
-
Excessive power rail ripple during motor switching events
-
Solder joint fatigue observed near power connectors
-
Thermal stress around gate driver and current sense components
-
Assembly yield variability across pilot production runs
GOPCBA Solution
GOPCBA implemented a reliability-driven industrial PCB assembly strategy focused on power integrity and mechanical robustness. Assembly process optimization began with a detailed design-for-assembly review, addressing pad geometry, via placement, and copper balance.
Solder paste volume and stencil apertures were refined to ensure consistent solder fillets on high-current components. Reflow profiles were optimized to match laminate Tg and copper mass distribution, minimizing thermal gradients during assembly.
Mechanical reinforcement strategies, including optimized connector anchoring and enhanced via plating thickness, were applied to reduce vibration-induced fatigue. Power distribution paths were assembled with controlled solder joint geometry to minimize parasitic inductance.
Measured Performance Results
| Test Item | Requirement | Measured Result |
|---|---|---|
| Power Rail Ripple | ≤50 mV | 19 mV |
| Solder Joint Fatigue | No cracks after test | Pass |
| Thermal Hotspot Reduction | Target ≥25% | 38% |
| Assembly Yield | ≥98% | 99.4% |
The optimized industrial PCB assembly demonstrated improved electrical stability and mechanical durability under simulated operating conditions.

Stackup Design & RF Implementation
Although motor drive and PLC platforms are primarily power and control oriented, stackup design remains essential for power integrity, EMI suppression, and mechanical stability during assembly.
Example Stackup for Motor Drive and PLC PCB
| Layer | Function | Material |
|---|---|---|
| L1 | Power Components / Control Signals | High-Tg FR-4 |
| L2 | Solid Ground Plane | Copper |
| L3 | Power Plane | Copper |
| L4 | Control and Communication Signals | High-Tg FR-4 |
| L5 | Ground Plane | Copper |
| L6 | Through-Hole Power Components | High-Tg FR-4 |
This stackup provides low-impedance return paths for switching currents, reducing ground bounce and EMI. Balanced copper distribution minimizes board warpage during reflow and wave soldering, supporting precise component placement and consistent solder joint formation.
Power integrity simulations using ADS and power integrity analysis tools evaluated transient voltage response under motor switching conditions. TDR measurements verified impedance consistency for communication interfaces after assembly. Thermal FEM analysis supported heat spreading optimization around power devices.
Environmental & Reliability Validation
Industrial PCB assemblies for motor drive and PLC platforms must meet stringent reliability requirements to ensure long-term field performance.
Reliability Test Summary
| Test Type | Condition | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Cycling | −40 °C ↔ 105 °C, 500 cycles | Pass |
| High-Temp Operating Life | 105 °C, 1000 hrs | Pass |
| Humidity Exposure | 85 °C / 85% RH | Pass |
| Vibration | Industrial motor profile | Pass |
| Mechanical Shock | 30 g | Pass |
| Solder Reflow Endurance | Multiple profiles | No degradation |
Post-test cross-section analysis confirmed intact via barrels and stable intermetallic layers in solder joints. Thermal FEM correlation with measured data validated uniform heat distribution, reducing localized mechanical stress during operation.
These results demonstrate that power integrity optimization and mechanically robust assembly practices significantly improve long-term reliability for motor drive and PLC PCB assemblies.
Engineering Summary & Contact
Optimizing power integrity and mechanical robustness is fundamental to reliable industrial PCB assembly for motor drive and PLC platforms. By combining appropriate material selection, balanced stackup design, controlled assembly processes, and rigorous validation, industrial PCB assemblies can withstand high current transients, vibration, and thermal stress throughout extended service lifetimes.
An engineering-driven approach to industrial PCB assembly reduces electrical noise, enhances mechanical durability, and ensures consistent manufacturing quality across production volumes. GOPCBA provides industrial PCB assembly services focused on power integrity optimization, mechanical robustness, and reliability validation to support demanding motor drive and PLC applications in modern factory automation systems.